- Your cart is empty
- Continue Shopping
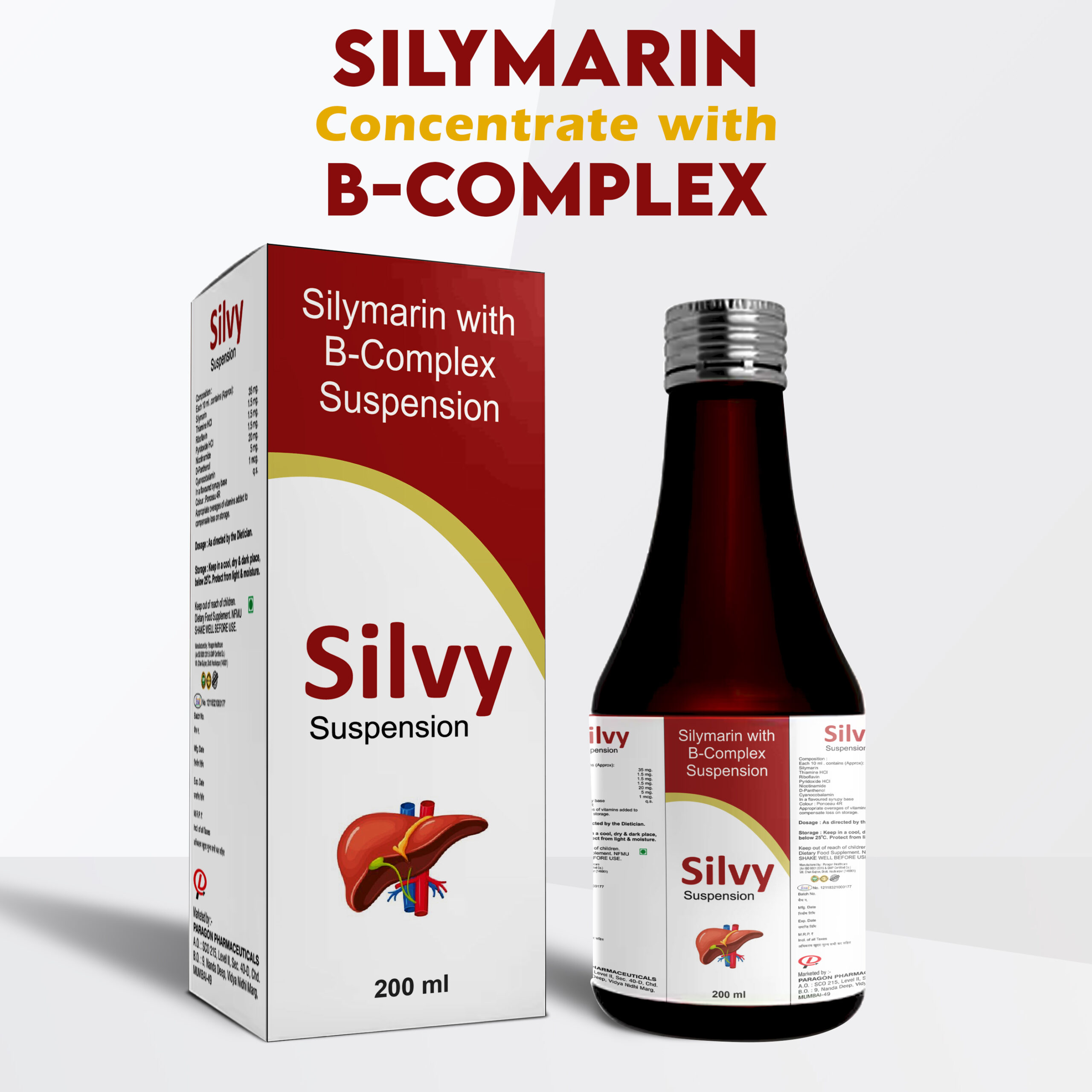
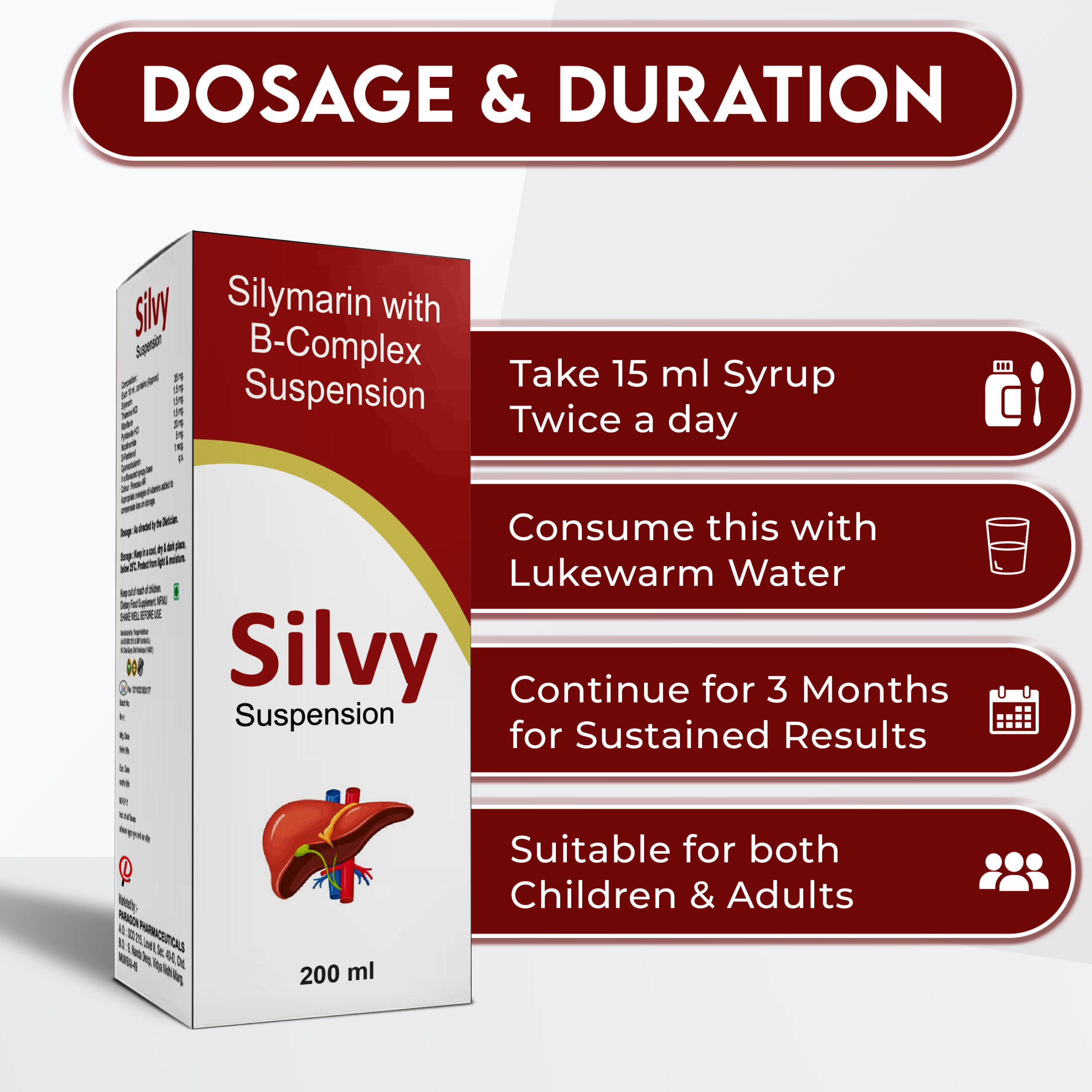
Silvy Suspension
₹154.00
Silvy Syrup for Liver Health- 200 ML (Pack of 1)
Silymarin with B-Complex Suspension for Liver Detoxification, Regeneration & Support for Healthy Liver Performance
Ingredients
Silvy Suspension is a unique combination of Silymarin, Thiamine, Riboflavin, Pyridoxine, Nicotinamide, etc.
About this Item
- Scientifically Researched Ayurvedic Formula: Silvy Syrup contains Herbal ingredients that help in strengthening the Liver by maintaining the liver cell membrane structure and promoting liver cell regeneration.
- Multipurpose Syrup: It is useful in improving Appetite & Digestion, relieving Gas, Constipation, Bloating, Abdominal Pain & Acidity.
- Manage Fatty Liver: It is helpful in managing fatty liver, jaundice, cholesterol levels, and other Liver Problems
- Promotes Digestion & Appetite: Silvy Syrup helps improve bile secretions, liver enzymatic parameters, and intestinal good bacteria.
- Regulates Cholesterol Levels: Silymarin helps in fat metabolism by stimulating the secretion of bile from the liver and has cholesterol-lowering effects.
- Anti-Oxidant Properties: Silymarin is a strong antioxidant that reduces the chances of oxidative stress-induced liver damage. Also, it helps to restore natural antioxidant GSH (glutathione) and SOD (superoxide dismutase) levels in the liver.
- Anti-Inflammatory Action: It contains anti-inflammatory herbs that protect the liver against alcoholic liver damage and are effective in bloating & abdominal pain.
Add to cart
Buy Now